In today’s quest for more sustainable and efficient energy production, Pelletierung stands out as an essential technology. From producing biomass fuel to processing feed for livestock, pelletiering has applications that touch multiple industries. This method, which compresses materials into small, dense pellets, is not just an efficient way to process raw materials but also provides environmental and economic benefits.
Let’s take a closer look at the pelletiering process, its advantages, and its wide array of uses.
What Is Pelletiering?
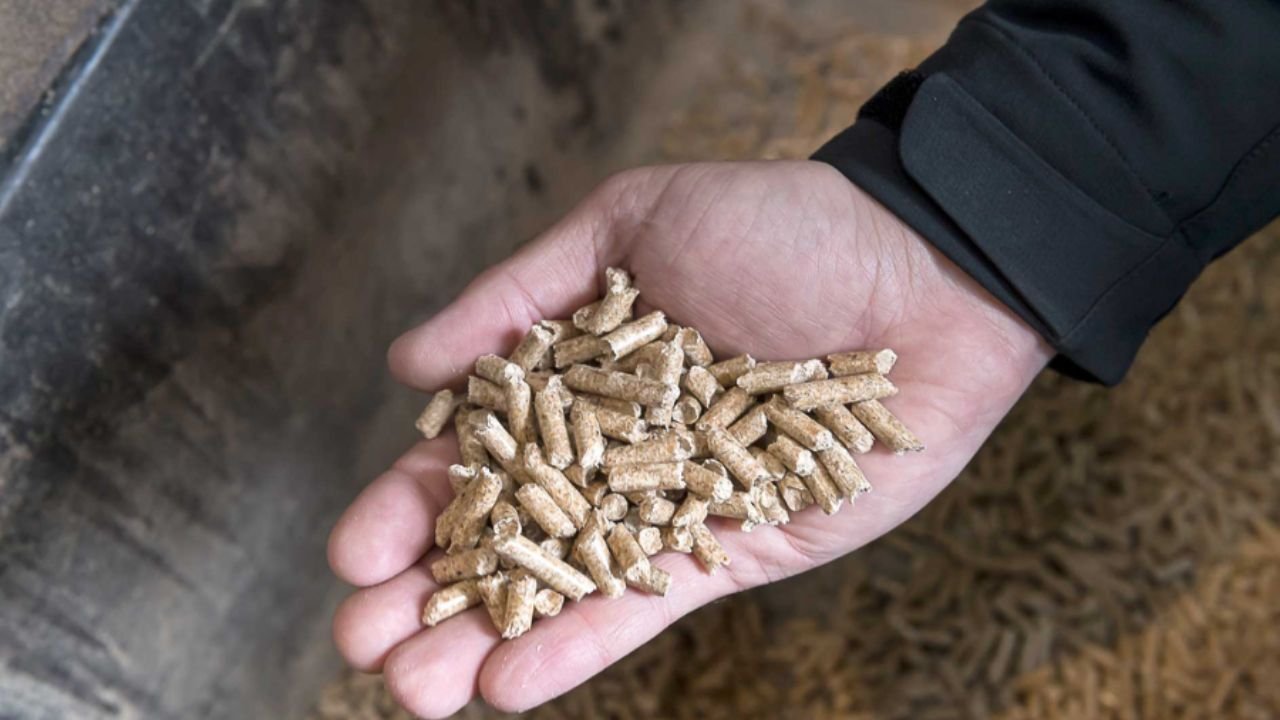
Pelletiering refers to the process of compressing or molding raw materials into small, cylindrical pellets. The process involves grinding materials, applying pressure and heat, and sometimes adding a binding agent to ensure the pellets hold their shape. The idea of pelletiering stems from the need to transform loose, raw materials into a compact and more manageable form. It significantly reduces the volume of the material, making it easier to store, transport, and utilize.
Why Is Pelletiering Important?
Pelletiering plays a critical role in both environmental sustainability and resource management. It allows for the efficient use of biomass, agricultural by-products, and even waste materials. By converting these raw materials into dense, uniform pellets, industries can enhance combustion efficiency, reduce transportation costs, and create a product that’s easy to handle.
The Pelletiering Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
Pellet production follows a straightforward process, but it’s essential to understand each step for the best results. The key stages include:
- Material Preparation: The first step involves grinding the raw material into fine particles to ensure uniform pellet formation. Common materials include wood chips, straw, sawdust, and even agricultural waste.
- Moisture Control: Maintaining the right moisture content is critical to the pellet’s structural integrity. Too much moisture weakens the pellets, while too little can cause brittleness.
- Pellet Pressing: The prepared material is fed into a pellet mill, where it’s subjected to high pressure and heat. The material is forced through a die, producing cylindrical pellets of uniform size.
- Cooling: Freshly pressed pellets are hot and soft. They need to cool down to harden and reach their final form.
- Screening and Packaging: The pellets are screened to remove any loose particles or dust, then packaged for transport or immediate use.
Advantages of Pelletiering
The benefits of pelletiering extend beyond just creating a compact product. Here are some notable advantages:
- Enhanced Efficiency: Pellets burn more efficiently than raw biomass, making them an excellent fuel choice for heating systems and industrial processes.
- Cost-Effective Storage and Transport: Pellets are dense and uniform, reducing the cost of storage and transportation.
- Eco-Friendly: Pelletiering allows for the recycling of waste products like sawdust and straw, turning what would otherwise be discarded into a valuable resource.
- Consistent Quality: The uniform size and density of pellets ensure consistent performance in combustion and feeding systems.
Pelletiering in Energy Production
One of the most significant applications of pelletiering is in biomass energy production. Wood pellets, made from sawdust, wood chips, and other organic materials, serve as an eco-friendly fuel for heating and power generation. These pellets provide a carbon-neutral alternative to fossil fuels, as they release only as much carbon dioxide during combustion as the plants absorbed during their growth cycle.
Pelletiering for Animal Feed
In the agricultural sector, pelletiering is widely used for producing animal feed. This process involves compressing various feed ingredients into dense pellets, ensuring that animals receive a balanced diet with every bite. Pelletized feed improves digestion, reduces wastage, and is easier to handle and store than loose feed.
Sustainable Practices in Pelletiering
Sustainability is at the heart of the pelletiering process, particularly in energy production. By using waste materials like sawdust, agricultural residues, and forest by-products, pellet production reduces landfill waste and contributes to cleaner energy solutions. Pellet plants that run on renewable energy sources further enhance the sustainability of the entire process.
Technological Innovations in Pelletiering
Recent advancements in pelletiering technology have made the process more efficient and environmentally friendly. Modern pellet mills are equipped with automated systems for monitoring moisture content, temperature, and pressure, ensuring optimal pellet quality with minimal energy consumption. Furthermore, the use of more durable materials in pellet press designs has reduced wear and tear, cutting down on maintenance costs.
Pellet Quality: Key Factors to Consider
When it comes to pelletiering, quality matters.
- Raw Material Consistency: Uniformity in the size and moisture content of raw materials is crucial for producing durable pellets.
- Pellet Mill Design: The design and condition of the pellet mill directly impact pellet quality. Worn dies and rollers can result in poor pellet formation.
- Temperature and Pressure: The right balance of heat and pressure during the pressing stage ensures the pellets are dense and durable.
Pelletiering and Its Environmental Impact
Pelletiering offers several environmental benefits, particularly in the realm of renewable energy. By converting waste materials into usable fuel or feed, it reduces the need for landfills and mitigates greenhouse gas emissions.
Also Read: Discover the Best Holistic Healthcare Products for Mind and Body
Challenges in the Pelletiering Industry
Despite its many benefits, the pelletiering industry faces several challenges. These include:
- Raw Material Supply: A steady and consistent supply of raw materials is essential for pellet production. Fluctuations in the availability of biomass can disrupt operations.
- Energy Consumption: While pelletiering is an efficient process, it still requires significant amounts of energy, particularly during the grinding and pressing stages.
Economic Benefits of Pelletiering
Pelletiering offers significant economic benefits, both for producers and end-users. For producers, the process allows them to turn waste materials into valuable products. For end-users, pellets provide a cost-effective and efficient fuel or feed option. In regions where biomass is abundant, pellet production can also stimulate local economies by creating jobs and encouraging the use of local resources.
Pelletiering in the Circular Economy
Pelletiering is a perfect example of a circular economy practice. By using waste materials from industries like forestry and agriculture, pellet production minimizes waste and maximizes resource efficiency.
Future Trends in Pelletiering
The pelletiering industry is poised for continued growth, particularly as demand for renewable energy sources increases. Future trends include:
- Increased Automation: As technology advances, more pellet plants are adopting automated systems to improve efficiency and reduce labor costs.
- Sustainability Initiatives: As environmental concerns become more pressing, the use of renewable energy in pellet plants and the sourcing of sustainable raw materials will likely become more common.
- Global Expansion: The demand for pellets is growing worldwide, particularly in countries that are investing in biomass energy as a way to reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
Pelletiering: A Key Component of a Sustainable Future
In conclusion, pelletiering offers a sustainable and efficient solution for transforming raw materials into usable products. Whether it’s producing fuel for heating systems, feed for livestock, or fertilizers for agriculture, the benefits of pelletiering are vast. As technology continues to improve and demand for renewable resources grows, pelletiering will remain a vital process in the transition toward a more sustainable future.
FAQs
What is pelletiering used for?
Pelletiering is primarily used to produce biomass fuel, animal feed, and fertilizers. It compresses raw materials into dense pellets for easier storage, transport, and use.
How does pelletiering benefit the environment?
Pelletiering benefits the environment by reducing waste, recycling organic materials, and providing a carbon-neutral fuel alternative in the form of biomass pellets.
What materials can be pelletized?
Common materials used in pelletizing include wood chips, sawdust, straw, corn stover, rice husks, and industrial waste like paper.
How is pellet quality ensured?
Pellet quality is ensured through careful control of raw material consistency, moisture content, and the conditions during pressing, such as temperature and pressure.
What challenges does the pelletiering industry face?
The pelletiering industry faces challenges such as fluctuations in raw material supply, high energy consumption, and market demand volatility.
What are the economic benefits of pelletiering?
Pelletiering offers economic benefits by turning waste materials into valuable products and providing a cost-effective fuel or feed solution for end-users.